- 574.50 KB
- 2022-04-29 14:43:24 发布
- 1、本文档共5页,可阅读全部内容。
- 2、本文档内容版权归属内容提供方,所产生的收益全部归内容提供方所有。如果您对本文有版权争议,可选择认领,认领后既往收益都归您。
- 3、本文档由用户上传,本站不保证质量和数量令人满意,可能有诸多瑕疵,付费之前,请仔细先通过免费阅读内容等途径辨别内容交易风险。如存在严重挂羊头卖狗肉之情形,可联系本站下载客服投诉处理。
- 文档侵权举报电话:19940600175。
'《认识一元一次方程》第二课时参考课件
回顾:1、一元一次方程的概念:开学初,小明问他是数学老师:“老师,你今年几岁了?”数学老师想考考小明的智力,于是就这样回答:“我的年龄除以3乘以10,再加上20,刚好110。”你知道数学老师今年几岁吗?2、猜猜老师的年龄解:设数学老师今年x岁,则列方程得:
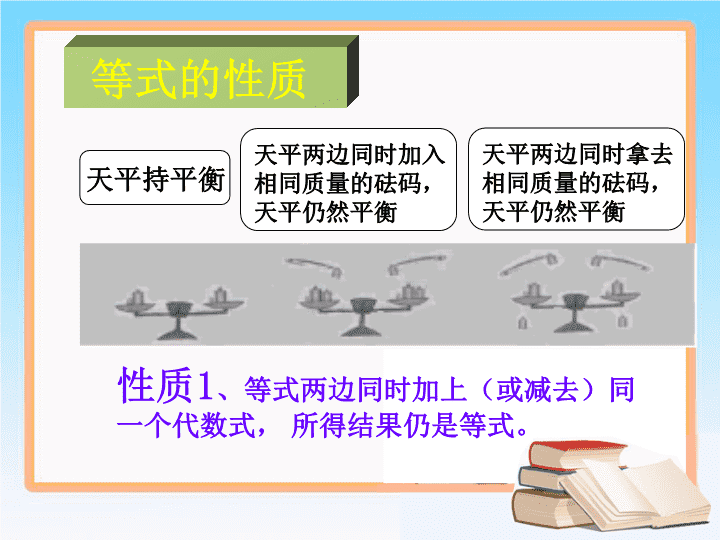
等式的性质性质1、等式两边同时加上(或减去)同一个代数式,所得结果仍是等式。天平持平衡天平两边同时加入相同质量的砝码,天平仍然平衡天平两边同时拿去相同质量的砝码,天平仍然平衡
随堂练习1、解下列方程:(1)x–9=8;(2)5–y=-16(3)3x+4=-13(4)2-3x–1=52、小红编了一道这样的题:我是4月出生的,我的年龄的2倍加上8,正好是我出生那一月的总天数。你猜我有几岁?请你求出小红的年龄。
3、选择:(1)下列说法正确的是()A.含有一个未知数的等式叫一元一次方程。B.未知数的次数是1的方程叫一元一次方程。C.含有一个未知数,并且未知数的次数是1的
整式叫一元一次方程。D.不是一元一次方程。+x=13-xD(2)下列式子中是一元一次方程的是()A.2x+y=4B.5x–2x2=1
C.3x–2=4D.5x–2C(3)使等式3x=x+3成立的x的值是()
A.x=-2B.x=3/2
C.x=¾D.x=-3/2B
4、填空(1)只含有未知数,并且未知数的次数是,系数不为,这样的方程叫做一元一次方程。(2)由4x=-2x+1可得出4x+=1.(3)由等式3x+2=6的两边都,得3x=4.(4)由方程–2x=4,两边同时乘以,得x=-2.(5)在等式5y–4=6中,两边同时,可得到5y=10,再两边同时,可得到y=2。一个102x减去2-1-2加上4除以5
小结本节课你学到什么知识?1、等式的基本性质。2、运用等式的基本性质解一元一次方程。注意:当我们获得了方程解的后还应检验,要养成检验的习惯。
作业布置P134习题5.2知识技能1问题解决4、5、6、7
会计报表和财务管理
会计报表资产负债表,损益表,现金流量表常用会计指标DuPontChart流行财务模型介绍EVA&MVA;CAPM&SML;GordenModel企业兼并Why(Synergy),WhichTypesHow(Example,CaseStudy)会计报表和财务管理
Cash7,28257,600AR632,160351,200Inventories1,287,360715,200TotalCA1,926,8021,124,000GrossFA1,202,950491,000Less:Deprec.263,160146,200NetFA939,790344,800TotalAssets2,866,5921,468,80019971996BalanceSheet:Assets
19971996Acctspayable524,160145,600Notespayable720,000200,000Accruals489,600136,000TotalCL1,733,760481,600Long-termdebt1,000,000323,432Commonstock460,000460,000Retainedearnings(327,168)203,768Totalequity132,832663,768TotalL&E2,866,5921,468,800BalanceSheet:LiabilitiesandEquity
Sales5,834,4003,432,000COGS5,728,0002,864,000Otherexpenses680,000340,000Deprec.116,96018,900Tot.op.costs6,524,9603,222,900EBIT(690,560)209,100Interestexp.176,00062,500EBT(866,560)146,600Taxes(40%)(346,624)58,640Netincome(519,936)87,96019971996IncomeStatement(P/LSheet)
(523,936)OPERATINGACTIVITIESNetincome(519,936)Add(sourcesofcash):Depreciation116,960IncreaseinAccts.Payable378,560Increaseinaccruals353,600Subtract(usesofcash):IncreaseinAccts.Receivable(280,960)Increaseininventories(572,160)Netcashprovidedbyops.StatementofCashFlow(1997)
StatementofCashFlows(1997)L-TINVESTINGACTIVITIESInvestmentinfixedassets(711,950)FINANCINGACTIVITIESIncreaseinnotespayable520,000Increaseinlong-termdebt676,568Paymentofcashdividends(11,000)Netcashfromfinancing1,185,568NETCHANGEINCASH(50,318)Plus:Cashatbeginningofyear57,600Cashatendofyear7,282
TheDuPontsystemfocuseson:ExpensecontrolAssetutilizationDebtutilization
DuPontEquationsROA=Profitmargin*TotalassetsturnoverROE=ROA*EquitymultiplierROE=(Profitmargin)(Totalassetturnover)(Equitymultiplier)=Netincome/sales*sales/TotalAssets*Totalassets/Commonequity
TheotherkeyratiosP/Eratio=Themarketpriceofstock/EPSEPS=Earnings/ThesharesoutstandingWhatisyouridea?
MVA&EVA(1)MVA:MarketValueAddedThedifferencebetweenthemarketvalueofequityandtheamountofequitycapitalthatinvestorssuppliedMVA=Marketvalueofequity-Equitycapitalsuppliedbyinvestors=(Sharesoutstanding)(StockPrice)-Totalcommonequity
MVA&EVA(2)MVAExampleCoca-Colain1995MarketvalueofEquity:$69bTotalcommonequity:$8bMVA:$61bEPS:$8.63GMin1995MarketvalueofEquity:$69bTotalcommonequity:$87bMVA:$18bEPS:$0.79
MVA&EVA(3)EVA:EconomicValueAddedValueaddedtoshareholdersbymanagementduringagivenyearTomeasuretheeffectsofmanagerialactionsEVA=After-taxoperatingprofit-After-taxcostoftotalcapital=EBIT(1-Corporatetaxrate)-After-taxcostoftotalcapitalTotalcapitalincludes:Long-termdebt,preferredstock,andcommonequity
MVA&EVA(4)EVAcasestudyCSXCorporationin1988,stockprice$28BU:Locomotive,containers,trailer,railcarsEVAapproachlost$70MSellingoff,increasingvolumeTill1993,stockprice$82.5
MVA&EVA(5)Securityanalysts:ThestockpricestrackEVAfarmorecloselythanotherfactorssuchasEPS,ROEandOperatingMargin
CAPMModel&SML(1)CAPMCapitalAssetPricingModelSMLTheSecurityMarketLineSMLEquationRequiredreturnOnStockI=Risk-freerate+(Marketriskpremium)(Stock’sbeta)ORKi=KRF+(KM-KRF)biNote:KM,requiredrateofreturnonaportfolioconsistingofallstocks
CAPMModel&SML(2)Beta(bi):Ameasureoftheextenttowhichthereturnsonagivenstockmovewiththestockmarket.Betaisthetheoreticallycorrectmeasureofthestock’sriskness.
CAPMModel&SML(3)ThebetaofsomestocksStockBetaAmericaOnline2.10BallyEntertainment1.55MicrosoftCorp1.20GeneralElectric1.15Procter&Gamble1.05Coca-Cola1.00Heinz0.90EmpireDistrictElectric0.55Source:ValueLine,August16,1996
.T-billsSMLkM=15kRF=8-1012SML:ki=8%+(15%-8%)bi.ki(%)Risk,biCAPMModel&SML(4)
CAPMModel&SML(5)SML1OriginalsituationRequiredRateofReturnk(%)SML200.51.01.52.01815118NewSMLInvestorsraiseinflation
expectationsby3%
CAPMModel&SML(6)1.0kM=18%kM=15%SML1OriginalsituationRequiredRateofReturn(%)SML2AfterincreaseinriskaversionRisk,bi18158
GordenModel(ConstantGrowthModel)Toevaluatethestockpricewiththeconstantgrowthrate.P0=D0(1+g)/(Ks-g)P0theexpectedpriceofthestocktodayD0dividendthestockholderexpectstoreceivetodayKsrequiredreturnrategexpectedgrowthrate
Whydomergersoccur?Synergy“2Plus2Equals5Effect”IfcompaniesA&BmergetoformCompanyC,andifC’svalueexceedsthatofA&Btakenseparately,thensynergyissaidtoexist.
OperatingEconomiesEconomicsofScalesinmanagement,marketing,production,ordistributionFinancialEconomiesLowertransactioncost,bettercoverageDifferentialManagementEfficiencyMoreefficiencyofthemanagementmoreproductivityoftheweakerfirm’sassetIncreasedmarketpowerReducedcompetitionSynergycouldarisefrom
TaxconsiderationAprofitablefirmacquiresafirmwithlargeaccumulatedtaxlossesPurchaseofassetbelowtheirreplacementcost(economicchoice)DiversificationManager’sPersonalincentivesTheotherreasonsofmergers
AhorizontalmergerInthesameindustry,suchastwoICPAverticalmergerSupplier-buyer,suchasIntel&DellAcongenericmergerTherelatedenterprises,suchasMicrosoft&IBMAconglomeratemergerTheunrelatedenterprises,suchasAmericanOnline&Time-WarnerTypeofMergers
AnalysisofapotentialmergerTheAcquiringFirmV.STheTargetFirmValuingthetargetfirmSettingthebidpricePostmergercontrolStructuringthetakeoverbidNote:thegoalofmergervaluationistovaluethetargetbusiness’sequitybecauseabusinessisacquiredfromitsowners,notfromitscreditors
MergerexampleTheacquringfirm:HightechThetargetfirm:ApexCorporationStep1:ValuingthetargetfirmDiscountedCashFlowApproach(DCF)GordenModelandCAPMStep2:SettingthebidpriceThedifferencebetweenApex’sMVAandtheevaluatedpriceOffercashorsecuritiesThenegotiatingskillsofthebothsidesThebargainingpositionsasdeterminedbyfundamentaleconomicsituation…..Step3PostmergercontrolHowtore-positiontheoldmanagementStep4TakeoverAction
MergerCaseStudyTheacquiringfirm:Smitty’sHomeRepairThetargetfirmHill’sHardwareYoushouldIdentifywhichtypeofmergeritisTakeDCFanalysisTakethescopeofyourbidPresentyourdecisionsin10minuteswithlessthan5slides'
您可能关注的文档
- 最新《葡萄沟》课件课件PPT.ppt
- 最新《蚂蚁的救助》2课件(语文S版三年级下册课件)课件PPT.ppt
- 最新《行路难》公开课课件课件PPT.ppt
- 最新《行路难+其一+》课件PPT课件.ppt
- 最新《观察三个正方体组成的物体》名师课件课件PPT.ppt
- 最新《解比例》课件PPT课件ppt.ppt
- 最新《解决实际问题》原创课件课件PPT.ppt
- 最新《解三角形》章节复习课课件课件PPT.ppt
- 最新《认识分米和毫米》课件PPTppt课件.ppt
- 最新《认识正方体》课件1课件PPT.ppt
- 最新《认识比例尺》优质课课件PPT课件.ppt
- 最新《认识平行四边形》课件课件PPT.ppt
- 最新《记金华的双龙洞》课件解析课件PPT.ppt
- 最新《讲究卫生、预防疾病》主题班会0328课件PPT.ppt
- 最新《让我——的一件事》作文指导课件(1)课件PPT.ppt
- 最新《设计生活标志》课件课件PPT.ppt
- 最新《论语》选读:《仁者爱人》课件课件PPT.ppt
- 最新《论语》十二章ppt课件正式-(1)课件PPT.ppt