- 5.06 MB
- 2022-04-29 14:23:35 发布
- 1、本文档共5页,可阅读全部内容。
- 2、本文档内容版权归属内容提供方,所产生的收益全部归内容提供方所有。如果您对本文有版权争议,可选择认领,认领后既往收益都归您。
- 3、本文档由用户上传,本站不保证质量和数量令人满意,可能有诸多瑕疵,付费之前,请仔细先通过免费阅读内容等途径辨别内容交易风险。如存在严重挂羊头卖狗肉之情形,可联系本站下载客服投诉处理。
- 文档侵权举报电话:19940600175。
'5细菌的遗传和变异e
BacterialGenomics
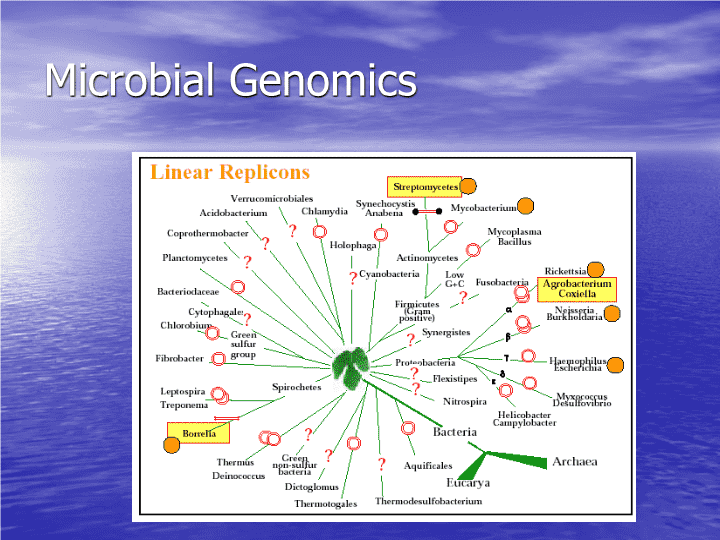
MicrobialGenomics
PLASMIDSPlasmidsareextrachromosomalgeneticelementscapableofautonomousreplication.AnepisomeisaplasmidthatcanintegrateintothebacterialchromosomeClassificationofPlasmidsTransferpropertiesConjugativeplasmidsNonconjugativeplasmidsPhenotypiceffectsFertilityplasmid(Ffactor)Bacteriocinogenicplasmids.Resistanceplasmids7factors).
Insertionsequences(IS)-Insertionsequencesaretransposablegeneticelementsthatcarrynoknowngenesexceptthosethatarerequiredfortransposition.a.Nomenclature-InsertionsequencesaregiventhedesignationISfollowedbyanumber. e.g.IS1b.StructureInsertionsequencesaresmallstretchesofDNAthathaveattheirendsrepeatedsequences,whichareinvolvedintransposition.Inbetweentheterminalrepeatedsequencestherearegenesinvolvedintranspositionandsequencesthatcancontroltheexpressionofthegenesbutnoothernonessentialgenesarepresent.c.Importancei)Mutation-Theintroductionofaninsertionsequenceintoabacterialgenewillresultintheinactivationofthegene.ii)Plasmidinsertionintochromosomes-Thesitesatwhichplasmidsinsertintothebacterialchromosomeareatornearinsertionsequenceinthechromosome.iii)PhaseVariation-Theflagellarantigensareoneofthemainantigenstowhichtheimmuneresponseisdirectedinourattempttofightoffabacterialinfection.InSalmonellatherearetwogeneswhichcodefortwoantigenicallydifferentflagellarantigens.Theexpressionofthesegenesisregulatedbyaninsertionsequences.Inoneorientationoneofthegenesisactivewhileintheotherorientationtheotherflagellargeneisactive.Thus,Salmonellacanchangetheirflagellainresponsetotheimmunesystems"attack.PhasevariationisnotuniquetoSalmonellaflagellarantigens.Itisalsoseenwithotherbacterialsurfaceantigens.Alsothemechanismofphasevariationmaydifferindifferentspeciesofbacteria(e.g.Neisseria;transformation).
Transposons(Tn)-Transposonsaretransposablegeneticelementsthatcarryoneormoreothergenesinadditiontothosewhichareessentialfortransposition.Nomenclature-TransposonsaregiventhedesignationTnfollowedbyanumber.Structure-Thestructureofatransposonissimilartothatofaninsertionsequence.Theextragenesarelocatedbetweentheterminalrepeatedsequences.Insomeinstances(compositetransposons)theterminalrepeatedsequencesareactuallyinsertionsequences.Importance-Manyantibioticresistancegenesarelocatedontransposons.SincetransposonscanjumpfromoneDNAmoleculetoanother,theseantibioticresistancetransposonsareamajorfactorinthedevelopmentofplasmidswhichcanconfermultipledrugresistanceonabacteriumharboringsuchaplasmid.Thesemultipledrugresistanceplasmidshavebecomeamajormedicalproblembecausetheindiscriminateuseofantibioticshaveprovidedaselectiveadvantageforbacteriaharboringtheseplasmids.
MechanismofbacterialvariationGenemutationGenetransferandrecombinationTransformationConjugationTransductionLysogenicconversionProtoplastfusion
TypesofmutationBasesubstitutionFrameshefitInsertionsequences
Whatcancausemutation?Chemicals:nitrousacid;alkylatingagents5-bromouracilbenzpyreneRadiation:X-raysandUltravioletlightViruses
BacterialmutationMutationrateMutationandselectivityBackwardmutation
TransformationTransformationisgenetransferresultingfromtheuptakebyarecipientcellofnakedDNAfromadonorcell.Certainbacteria(e.g.Bacillus,Haemophilus,Neisseria,Pneumococcus)cantakeupDNAfromtheenvironmentandtheDNAthatistakenupcanbeincorporatedintotherecipient"schromosome.
ConjugationTransferofDNAfromadonortoarecipientbydirectphysicalcontactbetweenthecells.Inbacteriatherearetwomatingtypesadonor(male)andarecipient(female)andthedirectionoftransferofgeneticmaterialisoneway;DNAistransferredfromadonortoarecipient.
PhysiologicalStatesofFFactorAutonomous(F+)CharacteristicsofF+xF-crossesF-becomesF+whileF+remainsF+LowtransferofdonorchromosomalgenesF+
PhysiologicalStatesofFFactorIntegrated(Hfr)CharacteristicsofHfrxF-crossesF-rarelybecomesHfrwhileHfrremainsHfrHightransferofcertaindonorchromosomalgenesF+Hfr
PhysiologicalStatesofFFactorAutonomouswithdonorgenes(F’)CharacteristicsofF’xF-crossesF-becomesF’whileF’remainsF’HightransferofdonorgenesonF’andlowtransferofotherdonorchromosomalgenesHfrF’
MechanismofF+xF-CrossesDNAtransferOriginoftransferRollingcirclereplicationPairformationConjugationbridgeF+F-F+F-F+F+F+F+
MechanismofHfrxF-CrossesDNAtransferOriginoftransferRollingcirclereplicationHomologousrecombinationPairformationConjugationbridgeHfrF-HfrF-HfrF-HfrF-
MechanismofF’xF-CrossesDNAtransferOriginoftransferRollingcirclereplicationPairformationConjugationbridgeF’F’F’F’F’F-F’F-
RPlasmid
Transduction:Transductionisdefinedasthetransferofgeneticinformationbetweencellsthroughthemediationofavirus(phage)particle.ItthereforedoesnotrequirecelltocellcontactandisDNaseresistant.
GeneralizedTransductionGeneralizedtransductionistransductioninwhichpotentiallyanybacterialgenefromthedonorcanbetransferredtotherecipient.
Themechanismofgeneralized
transduction
GeneralizedtransductionItisrelativelyeasy.Itisratherefficient(10-3perrecipientwithP22HT,10-6withP22orP1),usingthecorrectphage.Itmovesonlyasmallpartofthechromosomewhichallowsyoutochangepartofastrain"sgenotypewithoutaffectingtherestofthechromosome.Thehighfrequencyoftransferandthesmallregiontransferredallowsfine-structuremapping
SpecializedtransductionSpecializedtransductionistransductioninwhichonlycertaindonorgenescanbetransferredtotherecipient.DifferentphagesmaytransferdifferentgenesbutanindividualphagecanonlytransfercertaingenesSpecializedtransductionismediatedbylysogenicortemperatephageandthegenesthatgettransferredwilldependonwheretheprophagehasinsertedinthechromosome.
Themechanismofspecializedtransduction
SpecializedtransductionVeryefficienttransferofasmallregion--canbeusefulforfine-structuremappingExcellentsourceofDNAforthechromosomalregioncarriedbythephage,sinceeveryphagecarriesthesameDNA.Canoftenbeusedtoselectfordeletionsofsomeofthechromosomalgenescarriedonthephage.Merodiploidsgeneratedusingspecializedphagecanbequiteusefulincomplementationanalyses.
LysogenicconversionTheprophageDNAasagenerecombinedwithchromosomeofhostcell.
ProtoplastFusionFusionoftwoprotoplaststreatedwithlysozymeandpenicillin.
ApplicationofBacterialVariationUseinmedicalclinic:Diagnosis,Treatment,Prophylaxis.UseinGeneticEngineering
在Word2000中要完成各种编辑功能应遵循“先选定后操作”的原则。文本的编辑
在文本输入后,往往要对内容进行编辑,有删除、插入、移动、复制、撤消等,这些编辑大多在“常用工具栏”中有专门的按钮,以便于快速操作。编辑
方法一:Backspace键(←退格键)删除光标前的一个字符方法二:Delete键删除光标后的一个字符删除举例讨论:同样可以用作删除功能的Backspace键和Delete键的区别。
在默认情况下屏幕处于“插入”状态。此时先定位插入点,直接输入要插入的字符即可。如当前处于“改写”状态,则按键盘上的insert键或双击状态栏中的“改写”选项使之反白就表示已处于“插入”状态。举例插入
讨论在Windows窗口中文件(夹)的移动如何进行?移动方法2:用鼠标直接拖动方法1:选定剪切定位粘贴文本的选定
方法1:①选定要移动的内容;②按住鼠标左键可看到指针改变了形状;③拖动鼠标指针(指针移动的同时插入点也在移动);④到目的位置后松开鼠标。方法2:①选定要移动的内容;②单击工具栏中的“剪切”按钮;③定目的位置;④单击工具栏中的“粘贴”按钮。移动举例
复制讨论在Windows窗口中文件(夹)的复制如何进行?方法1:选定复制定位粘贴方法2:按住Ctrl键不放用鼠标直接拖动
方法1:①选定要复制的内容;②按住Ctrl键同时按住鼠标左键可看到指针改变了形状;③拖动鼠标指针(在指针移动的同时插入点也在移动);④到目的位置后松开鼠标和Ctrl键。方法2:①选定要复制的内容;②单击工具栏中的“复制”按钮;③定目的位置;④单击工具栏中的“粘贴”按钮。复制举例
练习文本的编辑
讨论:文本的移动(复制)可以在同一文档的任意距离间进行,也可以在不同文档间进行,用命令(按钮)的方法和用鼠标拖动的方法分别适合哪种情况?结论:若在同一文档的较长距离间或在不同文档中移动(复制)文本可通过命令(按钮)来实现。若在同一文档的较短距离间移动(复制)文本可用鼠标拖动的方法来实现。
1.选择任意文本:将光标定位在选择点开始处,按住鼠标左键拖动到结束点释放就可以选中文本。2.利用选择条快速选取:选择条是位于正文左边一个看不见的区域,将鼠标移到工作窗口的最左边,指针就会变成右斜箭头,表明鼠标已位于选择条中。如果在选择条中拖动鼠标可选定多行或多段文本单击鼠标可选定光标所在的一整行在选择条中双击鼠标可选定光标所在的一整段三击鼠标可选定整个文档选定文本
习题:删除句子中“美丽”一词:“我爱我们美丽的校园。”删除方法:一、如把光标定位在“美丽”的前面,则应按?键delete二、如把光标定位在“美丽”的后面,则应按?键←
插入习题:在句子“我爱我们的校园。”中加入“美丽”一词。方法:先定位光标如当前处于?状态则可直接输入“美丽”一词。“插入”如当前处于?状态则需要先改变状态再输入“美丽”一词。“改写”
移动习题:交换“文本编辑”两词的位置。方法:1.先选定“文本”一词,单击工具栏中“”按钮,然后定光标在“编辑”一词的后面,单击工具栏中的“”按钮。2.先选定“文本”一词,单击所选定的句子鼠标指针到“编辑”一词的后面,松开鼠标。剪切粘贴
复制习题:将句子“我爱我们的校园。”复制进括号。()方法:1.先选定句子“我爱我们的校园。”,单击工具栏中的“”按钮,然后定光标在括号中,单击工具栏中的“”按钮。2.先选定句子“我爱我们的校园。”,按住键不放,单击所选定的句子拖动鼠标指针到括号中,松开鼠标。Ctrl粘贴复制'
您可能关注的文档
- 最新5应用一元一次方程——“希望工程”义演pptx-31课件PPT.ppt
- 最新5平面连杆机构及其设计总结课件PPT.ppt
- 最新5消费者的个性心理与消费者行为课件PPT.ppt
- 最新5月网上授课—急性胰腺炎病人的护理孙桂玲课件PPT.ppt
- 最新5的乘法口诀课件PPT.ppt
- 最新5犬疱疹病毒感染课件PPT.ppt
- 最新5章医院膳食的种类课件PPT.ppt
- 最新5第一部分-组合体的投影(2)课件PPT.ppt
- 最新5芳酸及其酯类药物分析解析课件PPT.ppt
- 最新5课--第3课时--善用法律课件PPT.ppt
- 最新5软骨组织和软骨课件PPT.ppt
- 最新5骨关节疾病的社区康复课件PPT.ppt
- 最新5项目五食品酸度的测定苹果概述课件PPT.ppt
- 最新5非平衡载流子的产生与复合课件PPT.ppt
- 最新5除得尽吗资料课件PPT.ppt
- 最新6 Sigma BB 培训资料 26 C Continuous data SPC课件PPT.ppt
- 最新6-2多孔材料的合成化学课件PPT.ppt
- 最新6.1平方根第二课时课件课件PPT.ppt